
The latest n8n OpenAI node upgrade looks tiny in the UI, but it quietly decides whether your AI workflows sit on OpenAI’s future stack or its legacy one.
From n8n version 1.117.0, the OpenAI node V2 adds full support for the OpenAI Responses API and splits text operations into two distinct paths: Generate a Chat Completion (Chat Completions API) and Generate a Model Response (Responses API). See the docs. That second option is where the modern agent features now live.
At nocodecreative.io, this is exactly the level where we help clients: designing reliable, compliant AI workflows on n8n, Azure OpenAI, and Power Platform that slot into real CRMs, ERPs, and line-of-business systems rather than just powering a chat demo.
In this guide, we will look at what changed in the n8n OpenAI node, how the Responses API fits into your architecture, and three concrete workflow patterns you can use today, along with a pragmatic migration path off older Assistants-based flows.
Why this small change in the OpenAI node matters now
OpenAI has been clear about where things are heading: the Responses API is the long-term interface for building agents, tools, and structured-output workflows. The older Assistants API is being deprecated.
⚠️ Deprecation Timeline
Deprecation begins on 26 August 2025, with a full shutdown scheduled for 26 August 2026. Read the announcement.
At the same time, the Chat Completions API continues to be supported, and the Responses API is a superset of it. You can move only the flows that benefit from the new capabilities while leaving simple chat-style tasks on Chat Completions until you are ready.
That is exactly what n8n has now surfaced:
- Generate a Chat Completion maps to the Chat Completions API.
- Generate a Model Response maps to the Responses API and exposes additional controls.
For teams running production n8n workflows, this gives you a clear, low-friction migration path: new “smart” flows go to Responses, while existing light-touch prompts can stay on Chat Completions for now.
The shift from Assistants and Chat Completions to Responses
Historically, developers had to juggle three patterns when using OpenAI: Chat Completions for text-in/text-out, the Assistants API for complex agents with state, and a patchwork of function calling and JSON-mode tricks for structured data.
OpenAI is consolidating that into Responses + tools, featuring:
- A single API shape for text and JSON output.
- Built-in tools such as web search, file search, code interpreter, and computer use.
- Support for long-running background jobs and conversation objects.
n8n’s OpenAI node V2 explicitly removes support for the to-be-deprecated Assistants API and points those use cases to Responses instead.
What the deprecation timeline means for n8n flows
If you are already running n8n OpenAI workflows in production, the timeline dictates a clear strategy:
- Anything built on Assistants must move to Responses before 26 August 2026.
- New agent-like workflows should go straight to Generate a Model Response.
- Existing “single prompt in, single answer out” tasks can stay on Generate a Chat Completion, then be migrated gradually.
For UK and EU organisations with change governance and CAB processes, having this lead time is valuable. You can plan a sensible rollout rather than a frantic rewrite.
How the updated n8n OpenAI node works
At a high level, the OpenAI node now offers text operations including Chat Completion, Model Response, and Text Classification. It also supports richer workflows involving image, audio, file, video, and conversation operations.
The interesting bit for future-proofing is Generate a Model Response.
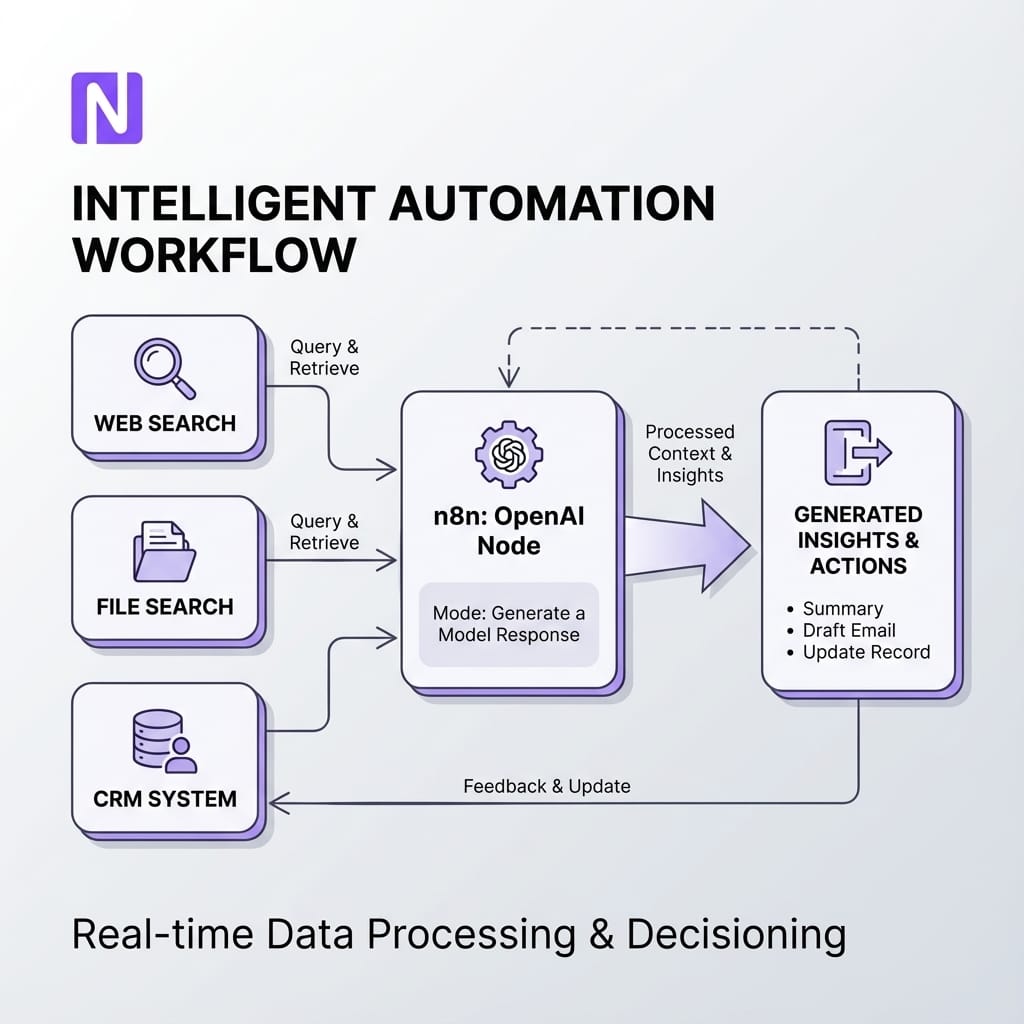
From “Message a model” to clear operations
In older n8n versions, the “Message a model” operation wrapped a mix of behaviours and mapped to Chat Completions. From version 1.117.0 onwards, this has been split. “Message a model” was renamed to Generate a Chat Completion, and Generate a Model Response was added as a distinct operation using the Responses API with explicit tool support.
This gives your automation team a clear rule of thumb:
Need simple chat behaviour or quick content? Use Generate a Chat Completion.
Need tools, files, JSON schema outputs or background processing? Use Generate a Model Response.
Key parameters for Responses mode in n8n
The Generate a Model Response operation exposes the core Responses concepts directly in the node:
Messages
You can send text, image, and file messages (currently PDFs via URL, file ID, or binary data). Each message has a role: user, assistant, or system. n8n defaults the system message to “You are a helpful assistant” but lets you override it.
Built-in tools
You can attach OpenAI-hosted tools including web search for live information, file search for uploaded documents, code interpreter for Python execution, and MCP servers for external toolchains. Both Chat Completion and Model Response operations support tool connectors via the AI tools system.
Output format
Combined with OpenAI’s structured outputs and JSON schema support, you can choose between plain text, JSON object (JSON mode), or JSON Schema-based format. This provides highly reliable JSON contracts back into your workflow.
Conversation & Background Mode
You can attach the call to a Conversation ID so input and output items are stored and reused for later turns, or continue from a Previous Response ID. Additionally, n8n exposes the Responses background flag, allowing you to run long jobs without blocking—ideal for deep research or heavy reporting.
When to use Chat Completions vs Responses in n8n
Both will be around for a while, so you do not need to panic-migrate everything. Instead, set a simple policy.
Keep Chat Completions for...
Simple prompts and legacy flows. Use this when you are doing lightweight content generation (subject lines, small rewrites), replying to users in plain text, or maintaining stable, low-risk flows.
Use Responses for...
Agents, tools, and JSON. Use this when you want reliable schema-based JSON outputs, need to call tools (search, APIs), require memory and background processing, or work in regulated environments.
In practice, many of your “serious” production flows will end up using Responses.
Workflow pattern 1 – Support email triage with structured JSON outputs
Support teams and shared inboxes are a perfect place to standardise on Responses. You typically need consistent categorisation, clean JSON objects for routing into ticket queues, and a clear audit trail for compliance.
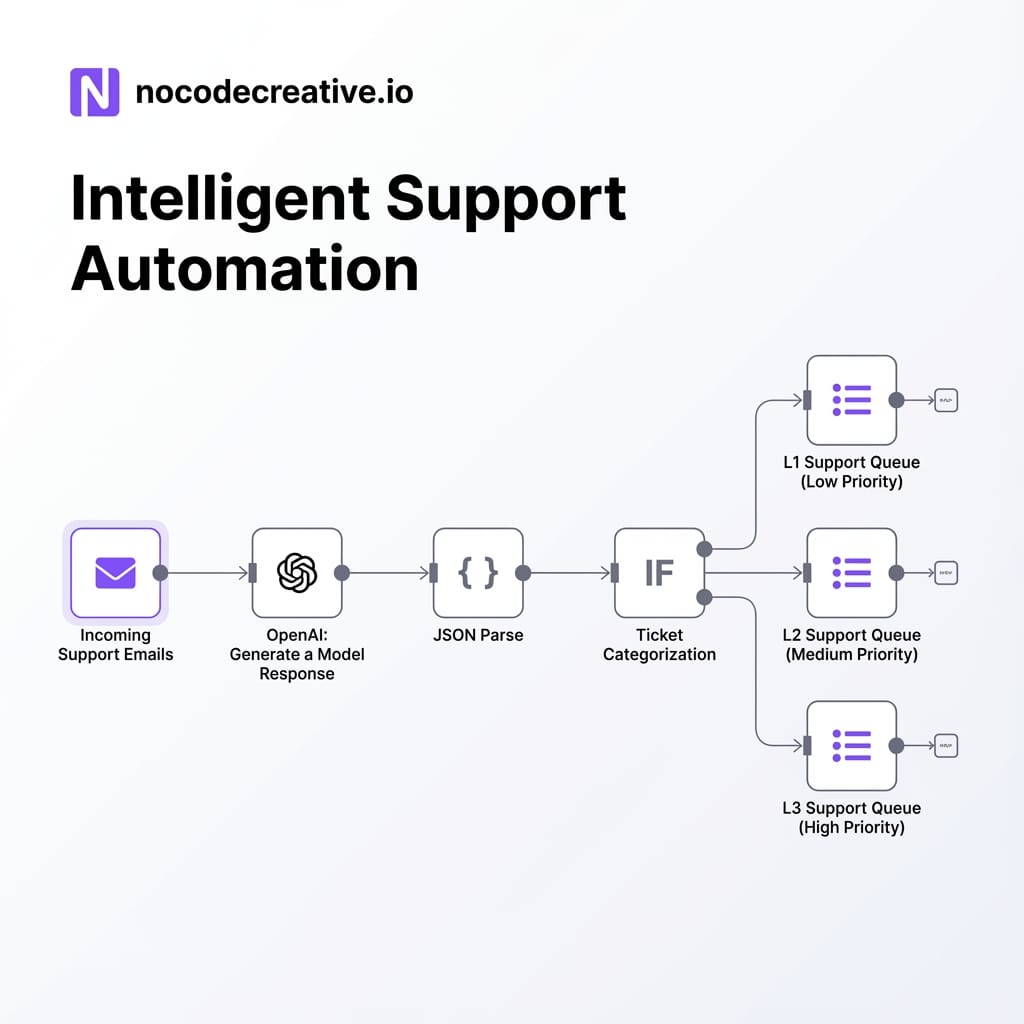
Node-by-node walkthrough
1. Trigger Node
Use IMAP/POP3, Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, or a helpdesk webhook. Extract the subject, body, sender, and relevant metadata.
2. Pre-processing (Optional)
Clean HTML to plain text and concatenate the subject, body, and key headers into a single text field.
3. OpenAI Node – Generate a Model Response
Set the resource to Text and use the Generate a Model Response operation. Provide a system message describing your triage policy and a user message with the email content. Crucially, set the Output format to JSON Schema to strictly define fields like intent, priority, product_area, and next_action.
4. JSON Parse & Routing
Parse the model output into standard JSON fields. Use IF nodes to route based on priority and intent, then create tickets in your helpdesk or escalate to Slack/Teams.
5. Logging
Log the raw input, model output, and routing decision to a database for observability.
This pattern uses Responses for what it does best: predictable JSON and tool support. If you later introduce file search for historical tickets or knowledge base articles, you are already using the correct operation.
Prompt and schema design for reliable automation
Two elements make this production-grade rather than a nice demo:
- Tight JSON schema: Use OpenAI’s structured outputs so the model is constrained to a schema and cannot “get creative” with extra fields.
- Robust error handling: Wrap the OpenAI node with a validation step that checks required fields and allowed enum values, implementing a fallback path for low-confidence results.
For teams who would rather not design this from scratch, nocodecreative.io implements similar patterns using n8n alongside Azure OpenAI or Microsoft 365 connectors.
Workflow pattern 2 – Sales co-pilot with web and CRM tools
Sales teams want more than a “chatbot”. They want an assistant that understands the account, the product catalogue, and the wider market, then surfaces concise recommendations into the CRM.
Exposing internal APIs as tools and orchestrating via Responses
The shape of a sales co-pilot flow in n8n involves triggering when an opportunity moves stage in your CRM (Salesforce, HubSpot, Dynamics). You then use n8n HTTP Request nodes to expose internal APIs as tools—getting account history, product options, or support tickets.
Using the Generate a Model Response node with tools enabled, you attach these connectors so the model can call internal APIs or perform web searches. The system instructions should clearly define how to use these tools and what structured answer is expected.
The model returns a structured object containing the account summary, risks, product recommendations, and draft outreach. n8n then writes these fields back into the CRM and sends drafts to Outlook or Gmail.
Hand-off into CRM, email and reporting
Because we now have structured data rather than free text:
- Your CRM can display the summary and recommendation fields directly in the opportunity form.
- Marketing systems can pick up “recommended next actions” for playbooks.
- You can run analytics over the generated suggestions to see how they correlate with win rates.
For organisations already using Microsoft tools heavily, we often mirror this design in Power Platform and Azure OpenAI, so the pattern is shared between n8n and Power Automate flows.
Workflow pattern 3 – Internal knowledge assistant with files and search
Support, operations, and compliance teams frequently need a safe way to query SOPs, contracts, and policy documents. The Responses API plus n8n’s connectors make this straightforward without building your own LLM stack from scratch.
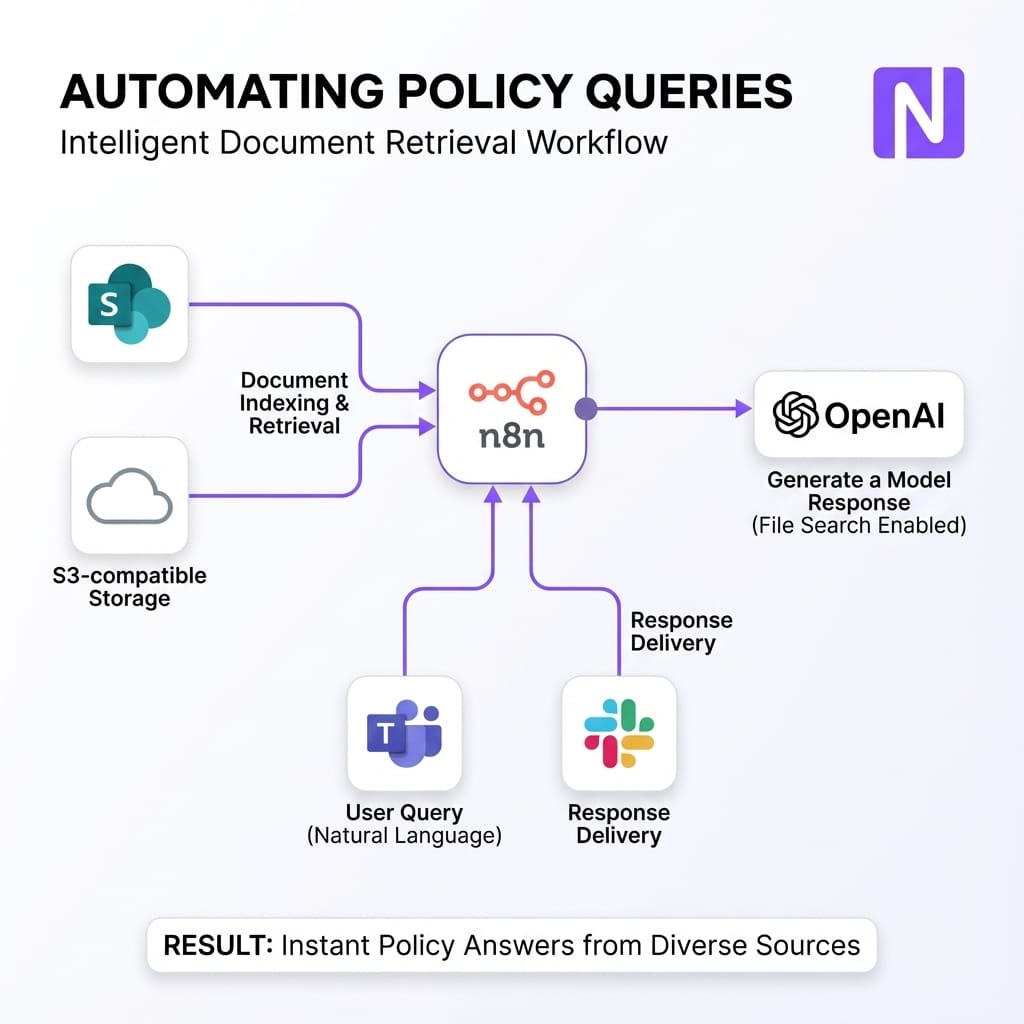
Feeding PDFs and documents into Responses via n8n
A robust knowledge assistant typically starts with document ingestion workflows that pull files from SharePoint or S3, normalize them, and upload them to OpenAI’s file storage. Metadata is stored alongside.
When a user asks a question via Teams or Slack, the Generate a Model Response node uses File Search tools to query uploaded content and Web Search for public regulations. The output is a structured object containing the answer, source citations, and a confidence score.
If the confidence is low or the topic is sensitive, the workflow routes the query to a human expert. This reduces the temptation for staff to paste sensitive documents into consumer tools while still giving them AI-powered answers.
Governance, logging and approval patterns
For enterprise and regulated environments, the key is governance:
- Auth: Use Microsoft 365 connectors and Azure AD to ensure the assistant only accesses documents the user is allowed to see.
- Logging: Store the question, retrieved documents, answer, and sources for audits.
- Approvals: For HR or finance topics, insert an approval node so a human signs off the draft before delivery.
Migration guide – Moving off Assistants-based n8n flows
If you have existing n8n automations using the older Assistants-based patterns, you can move gradually without breaking everything in one go.
Inventory your existing AI steps
Start with a simple inventory. List all n8n workflows using the OpenAI node. Capture the operation used, criticality, downstream systems touched, and whether it uses tools or files. Prioritise high-impact and high-risk flows.
Design an incremental rollout
Use OpenAI’s own recommendation: adopt Responses incrementally where it adds the most value first.
- New agent-like workflows: Build all new tool-using, file-searching, or JSON-heavy workflows on Generate a Model Response from day one.
- Migrate Assistants-based flows: Rewrite the assistant configuration as system instructions and tools for Responses. Move any thread logic into Conversations and Response IDs. Test side-by-side.
- Review simple Chat flows: Decide which flows gain from structured outputs. Move those to Responses; leave the others on Chat Completions.
- Retire unused flows: Tidy up old experiments that no longer serve a purpose.
Implementation checklist and common gotchas
Before you standardise on Responses in n8n, it is worth checking a few technical details.
Model selection, limits, and cost
Use modern models like GPT-4o or mini variants that support structured outputs. Set maximum tokens in the n8n node to control costs and combine retry logic with validation guards. Always log inputs, outputs, and tool calls to make debugging easier.
Security considerations
Apply the principle of least privilege: tools exposed to the model should have the narrowest access possible. Keep separate credentials and conversations for dev, test, and prod. For UK/EU organisations, verify if your usage aligns with Zero Data Retention (ZDR) policies, as some features like Structured Outputs may affect eligibility.
How we can help – From prototype to production AI workflows
The updated n8n OpenAI node gives you a clean way to standardise on the Responses API without burning down what already works. The bigger opportunity is to design a small set of reusable patterns: support triage, sales co-pilots, and knowledge assistants.
Once those patterns exist, your teams can reuse them across departments and platforms.
Ready to upgrade your automation stack?
If you would rather not design and harden all of this alone, nocodecreative.io specialises in intelligent workflow automation, AI agent orchestration, and low-code app development that fit neatly into your existing stack.
References
- OpenAI node documentation – operations and V2 overview
- OpenAI Text operations – Generate a Model Response
- Migrate to the Responses API – OpenAI guide
- Assistants migration guide – deprecating the Assistants API
- Introducing Structured Outputs in the API – OpenAI
- Tutorial: Build an AI workflow in n8n













